
|

| 产地 | 进口、国产 |
| 品牌 | 上海莼试 |
| 保存条件 | Store at -20 °C |
| 货号 | CS9874 |
| 应用范围 | WB=1:100-500 ELISA=1:500-1000 IP=1:20-100 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 |
| CAS编号 | |
| 抗体名 | Anti-NFKB1/p50 |
| 克隆性 | |
| 靶点 | 详见说明书 |
| 适应物种 | 详见说明书 |
| 形态 | 详见说明书 |
| 宿主 | 详见说明书 |
| 亚型 | IgG |
| 标识物 | 详见说明书 |
| 浓度 | 1mg/1ml% |
| 免疫原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from NFKB1 (51-100aa) |
产品订购信息:
英文名称 Anti-NFKB1/p50
中文名称 细胞核因子p50/k基因结合核因子抗体规格
别 名 DKFZp686C01211; DNA binding factor KBF1; DNA binding factor KBF1 EBP1; DNA binding factor KBF1 EBP1; DNA-binding factor KBF1; EBP 1; EBP-1; EBP1; KBF1; MGC54151; NF kappa B; NF kappabeta; NF kB1; NFKB 1; NFKB p105; NFKB p50; NFKB1; NFKB1_HUMAN; Nuclear factor kappa B DNA binding subunit; Nuclear factor NF kappa B p105 subunit; Nuclear factor NF kappa B p50 subunit; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells 1; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1; p84/NF-kappa-B1 p98.
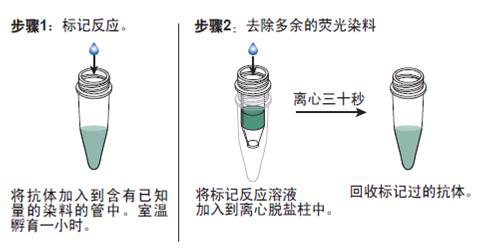

浓 度 1mg/1ml
规 格 0.1ml/100μg 0.2ml/200μg
抗体来源 Rabbit
克隆类型 polyclonal
交叉反应 Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Dog, Pig, Cow
产品类型 一抗
研究领域 细胞生物 染色质和核信号 信号转导 细胞凋亡 转录调节因子 表观遗传学
蛋白分子量 predicted molecular weight: 48/105kDa
性 状 Lyophilized or Liquid
免 疫 原 KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from NFKB1 (51-100aa)
亚 型 IgG
纯化方法 affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 with 10 mg/ml BSA and 0.1% Sodium azide
细胞核因子p50/k基因结合核因子抗体规格 产品应用 WB=1:100-500 ELISA=1:500-1000 IP=1:20-100 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500
(石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
保存条件 Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
Important Note This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
产品介绍 This gene encodes a 105 kD protein which can undergo cotranslational processing by the 26S proteasome to produce a 50 kD protein. The 105 kD protein is a Rel protein-specific transcription inhibitor and the 50 kD protein is a DNA binding subunit of the NF-kappa-B (NFKB) protein complex. NFKB is a transcription regulator that is activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant-free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. Activated NFKB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFKB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFKB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009].
Function : NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105.Subunit : Component of the NF-kappa-B p65-p50 complex. Component of the NF-kappa-B p65-p50 complex. Homodimer; component of the NF-kappa-B p50-p50 complex. Component of the NF-kappa-B p105-p50 complex. Component of the NF-kappa-B p50-c-Rel complex. Component of a complex consisting of the NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer and BCL3. Also interacts with MAP3K8. NF-kappa-B p50 subunit interacts with NCOA3 coactivator, which may coactivate NF-kappa-B dependent expression via its histone acetyltransferase activity. Interacts with DSIPI; this interaction prevents nuclear translocation and DNA-binding. Interacts with SPAG9 and UNC5CL. NFKB1/p105 interacts with CFLAR; the interaction inhibits p105 processing into p50. NFKB1/p105 forms a ternary complex with MAP3K8 and TNIP2. Interacts with GSK3B; the interaction prevents processing of p105 to p50. NFKB1/p50 interacts with NFKBIE. NFKB1/p50 interacts with NFKBIZ. Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit interacts with NFKBID. Directly interacts with MEN1. Interacts with HIF1AN.Subcellular Location : Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor (I-kappa-B).Post-translational modifications : While translation occurs, the particular unfolded structure after the GRR repeat promotes the generation of p50 making it an acceptable substrate for the proteasome. This process is known as cotranslational processing. The processed form is active and the unprocessed form acts as an inhibitor (I kappa B-like), being able to form cytosolic complexes with NF-kappa B, trapping it in the cytoplasm. Complete folding of the region downstream of the GRR repeat precludes processing.Phosphorylation at 'Ser-903' and 'Ser-907' primes p105 for proteolytic processing in response to TNF-alpha stimulation. Phosphorylation at 'Ser-927' and 'Ser-932' are required for BTRC/BTRCP-mediated proteolysis.Polyubiquitination seems to allow p105 processing.S-nitrosylation of Cys-61 affects DNA binding.The covalent modification of cysteine by 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin-J2 is autocatalytic and reversible. It may occur as an alternative to other cysteine modifications, such as S-nitrosylation and S-palmitoylation.Similarity : Contains 7 ANK repeats.Contains 1 death domain.Contains 1 RHD (Rel-like) domain.Database links : UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot: P19838.2转录调节因子(Transcriptin Regulators)

Anti-CK17/FITC 荧光素标记细胞角蛋白17抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Anti-Integrin Beta5/FITC 荧光素标记整合素β5抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Rhesus antibody Rh CCL4/MIP-1 Beta 巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1β抗体 规格 0.1ml
IL-2 (Interleukin-2)Human IL-2抗原(人) 0.5mg
HES3 英文名称: 转录因子HES3抗体 0.2ml
Rhesus antibody Rh SP-C 肺表面活性蛋白C抗体 规格 0.1ml
Anti-Integrin Beta5/FITC 荧光素标记整合素β5抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Mouse small nuclear ribonucleoprotein,snRNP/Sm ELISA Kit 小鼠抗小核糖核蛋白/Sm抗体Multi-class antibodies规格: 48T
Anti-phospho-Bim(Ser55) /FITC 荧光素标记兔抗人、大、小鼠磷酸化细胞死亡调解子抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Rhesus antibody Rh ER-Alpha 雌激素受体α抗体 规格 0.1ml
apo-B100 (Rabbit apoprotein B100) ELISA Kit 兔载脂蛋白B100 96T
MMP-2 英文名称: 基质金属蛋白酶2抗体 0.1ml
AE2 英文名称: 阴离子交换蛋白2抗体 0.2ml
Anti-phospho-Bim(Ser55) /FITC 荧光素标记兔抗人、大、小鼠磷酸化细胞死亡调解子抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Anti-GRB10/FITC 荧光素标记兔抗人、大、小鼠生长因子受体结合蛋白10抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Anti-p300/KAT3B/FITC 荧光素标记转录接头蛋白EP300抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
Rhesus antibody Rh beta-Actin (Loading Control) β-肌动蛋白抗体(内参抗体) 规格 0.1ml
CD133 造血干细胞抗原CD133 0.5mg
phospho-HSP70 (Tyr611) 英文名称: 磷酸化热休克蛋白-70抗体 0.1ml
Rhesus antibody Rh RAP1GAP RAP1GAP酶激活蛋白抗体 规格 0.2ml
Anti-p300/KAT3B/FITC 荧光素标记转录接头蛋白EP300抗体IgGMulti-class antibodies规格: 0.2ml
牛津琼脂基础26060用于单核增生李斯特氏菌的选择性分离(SN0005)。
GC 琼脂基础 (CM0367) Oxoid incubation media GC 琼脂基础 (CM0367) Oxoid
食酸菌 酸奶 支/瓶
VioletRedBileDextroseAgar
琼脂培养基M 250g 于肠杆菌科细菌的生化反应筛选。
改良的McBride琼脂MMA26030250g用于单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌的选择性分离培养(GB/T4789.30-2003,SN03)。
赖氨酸脱羧酶肉汤 (CM0308) Oxoid incubation media 赖氨酸脱羧酶肉汤 (CM0308) Oxoid
少根根霉 以正烷烃为碳源培养酵母,用此制成酵母膏和提取麦角固醇 支/瓶
大肠菌群、粪大肠菌群、大肠杆菌检验培养基
琼脂培养基H 250g 用于肠道致病菌的选择性分离培养。
细胞核因子p50/k基因结合核因子抗体规格 XLD琼脂颗粒培养基 规格: 10袋(300mL/袋) 用途: 用于临床标本及食品中沙门氏菌、志贺氏菌的选择性分离培养
营养肉汤颗粒培养基 规格: 10袋(300mL/袋) 用途: 用于一般细菌培养、复壮、增菌等,也可用于消毒剂定性消毒效果测定
大豆酪蛋白琼脂颗粒培养基 规格: 10袋(300mL/袋) 用途: 用于普通的或营养要求较高的细菌以及用于医药工业洁净室无菌程度的监测及消毒剂效果的测试
平板计数琼脂颗粒培养基 规格: 10袋(300mL/袋) 用途: 用于细菌总数测定

抗体的生物素化标记实验要点:
1. 细胞核因子p50/k基因结合核因子抗体规格 如在反应混合液中有叠氮钠或游离氨基存在,会抑制标记反应。因此,蛋白质在反应前要对 0.1mol/L碳酸氢钠缓冲液或0.5mol/L硼酸缓冲液充分透析;
2.所用的NHSB及待生物素化蛋白质之间的分子比按蛋白质表面的ε-氨基的密度会有所不同,选择不当则影响标记的效率,应先用几个不同的分子比来筛选最适条件;
3.用NHSB量过量也是不利的,抗原的结合位点可能因此被封闭,导致抗体失活;
4.由于抗体的氨基不易接近可能造成生物素化不足,此时可加入去污剂如 Triton x-100, Tween20等;
5.当游离ε-氨基(赖氨酸残基的氨基)存在于抗体的抗原结合位点时,或位于酶的催化位点时,生物素化会降低或损伤抗体蛋白的结合力或活性;
6.生物素还可能与不同的功能基团,如羰基、氨基、巯基、异咪唑基及*基,也可与糖基共价结合;
7.交联反应后,应充分透析,否则,残余的生物素会对生物素化抗体与亲和素的结合产生竞争作用;
8.在细胞的荧光标记实验中,中和亲和素的本底低,但由于链霉亲和素含有少量正电荷,故对某些细胞可导致高本底。
抗体的鉴定:
1)细胞核因子p50/k基因结合核因子抗体规格 抗体的效价鉴定:不管是用于诊断还是用于,制备抗体的目的都是要求较高效价。不同的抗原制备的抗体,要求的效价不一。鉴定效价的方法很多,包括有试管凝集反应,琼脂扩散试验,酶联免疫吸附试验等。常用的抗原所制备的抗体一般都有约成的鉴定效价的方法,以资比较。如制备抗抗体的效价,一般就采用琼脂扩散试验来鉴定。
2)抗体的特异性鉴定:抗体的特异性是指与相应抗原或近似抗原物质的识别能力。抗体的特异性高,它的识别能力就强。衡量特异性通常以交叉反应率来表示。交叉反应率可用竞争抑制试验测定。以不同浓度抗原和近似抗原分别做竞争抑制曲线,计算各自的结合率,求出各自在IC50时的浓度,并按公式计算交叉反应率。
如果所用抗原浓度IC50浓度为pg/管,而一些近似抗原物质的IC50浓度几乎是无穷大时,表示这一抗血清与其他抗原物质的交叉反应率近似为0,即该血清的特异性较好。
3)抗体亲和力:是指抗体和抗原结合的牢固程度。亲和力的高低是由抗原分子的大小,抗体分子的结合位点与抗原决定簇之间立体构型的合适度决定的。有助于维持抗原抗体复合物稳定的分子间力有氢键,疏水键,侧链相反电荷基因的库仑力,范德华力和空间斥力。亲和力常以亲和常数K表示,K的单位是L/mol。抗体亲和力的测定对抗体的筛选,确定抗体的用途,验证抗体的均一性等均有重要意义。